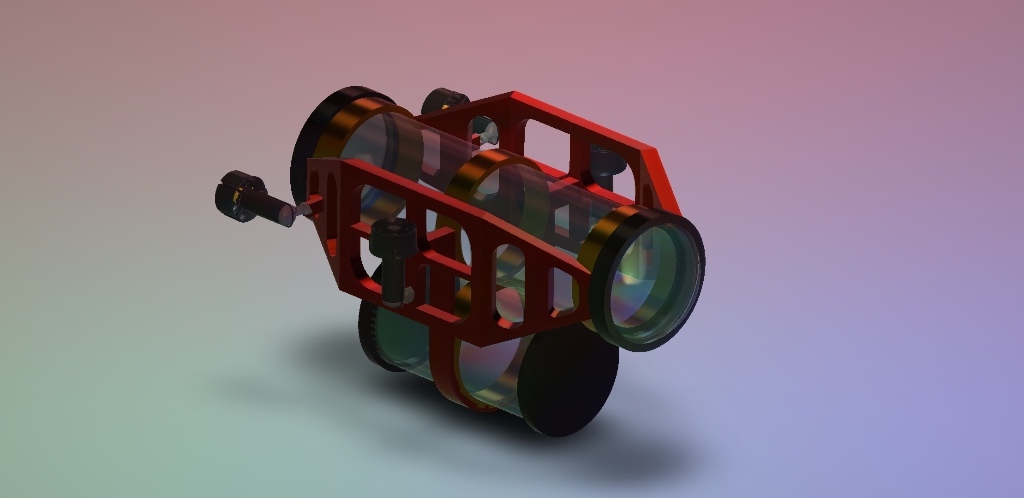
Mechonyx
AUV.
01 Introduction
An Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) is a self-propelled, unmanned robot designed to operate underwater without direct human intervention. E quipped with sensors, cameras, and navigation systems, AUVs are employed in diverse fields such as marine research, offshore exploration, underwater mapping, and environmental monitoring, revolutionizing our understanding of the underwater world.
- Autonomy and efficiency
- Enhanced Safety
- Data collection and accuracy
- Versitality
02 Description
AUV have become invaluable tools for various applications. The working principle of an AUV
includes the following.
1. Navigation and Control: Equipped with navigation
systems that utilize a combination of sensors and algorithms to
determine their position, orientation, and trajectory.
2. Mission Planning and Execution: Programmed with
predefined mission plans that dictate their tasks and routes.
3. Sensing and Data Collection: Equipped with a suite of
sensors to gather valuable data about the underwater environment.
4. Communication and Data Transmission: Capable to communicate with
surface vessels or shore-based stations.
5. Data Analysis and Post-Mission Processing : Collected data is then typically
processed and analyzed to extract valuable information.